New publication by Müller et al. (2024)
"Real-time navigation solutions of low-cost off-the-shelf GNSS receivers on board the Astrocast constellation satellites" by Müller et al. (2024)
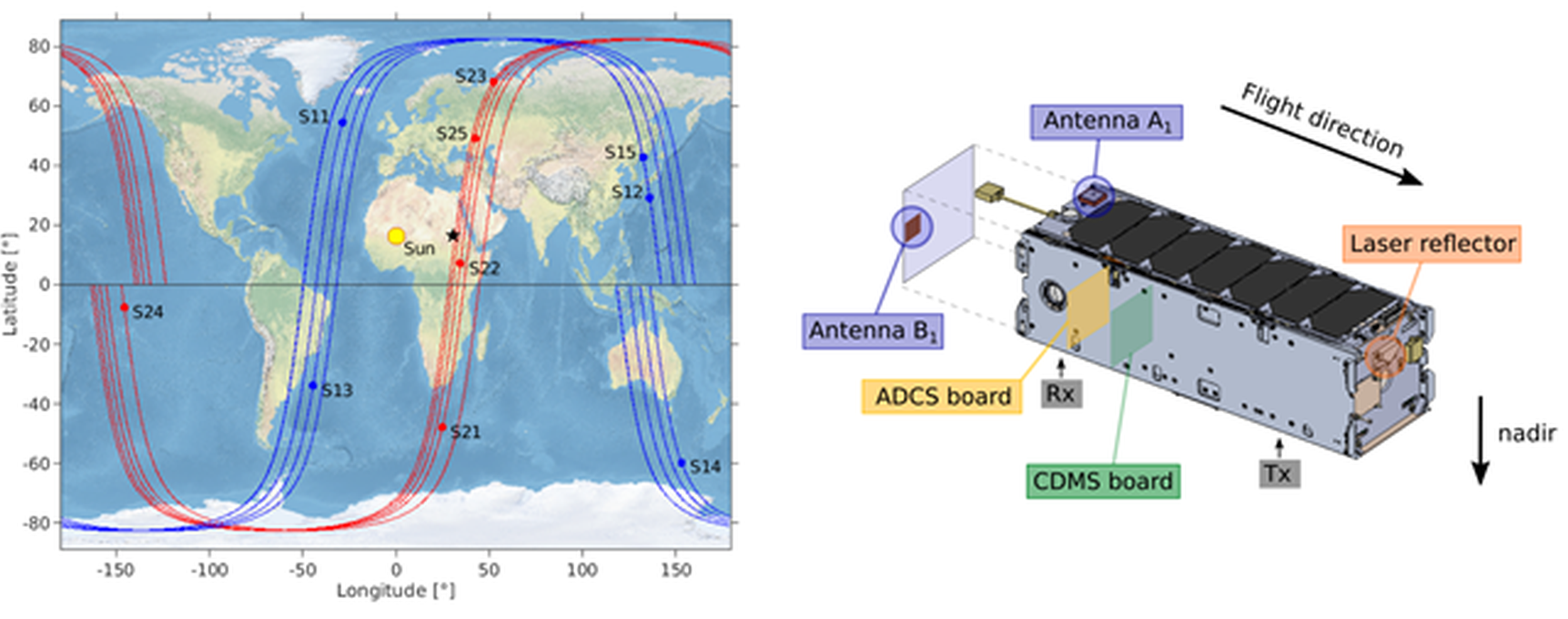
Global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) are increasingly being used on board small satellites for positioning and navigation in space. The CubeSats of the Swiss company Astrocast, which are equipped with our low-cost off-the-shelf single-frequency GNSS payload, have been providing near-continuous real-time navigation solutions (NAVSOL) for several years. Based on the in-flight data from 10 Astrocast satellites, this study analyses the performance of GNSS receivers on board small satellites, both in terms of temporal variations and differences between individual spacecrafts.
The paper shows that a low-cost GNSS payload can provide continuous real-time on-board positioning of small satellites with an accuracy of about 3 to 15 m at a very low price and with very low resources, but also points out three major effects that can degrade the NAVSOL accuracy by several meters: a radial offset due to ionospheric refraction, a periodicity of one revolution due to the high dynamics of the satellites, and interference of the GNSS signals with electromagnetic waves coming from different satellite subcomponents. These findings help to refine hardware configurations and firmware settings in preparation for future Astrocast satellites or other nanosatellite missions, so that real-time positioning with an accuracy of a few meters can be achieved.
Link to the article: external page https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2023.10.001