Enhancing GRACE Level-1 data processing with machine learning
Satellite gravimetry is a powerful technique used to measure variations in Earth's gravity field. The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellite mission, launched in 2002, was one of the most successful examples of satellite gravimetry. The data collected by the GRACE mission has led to groundbreaking discoveries in fields such as climate science, hydrology, and oceanography, and has provided unprecedented insights into the dynamic processes that shape our planet.
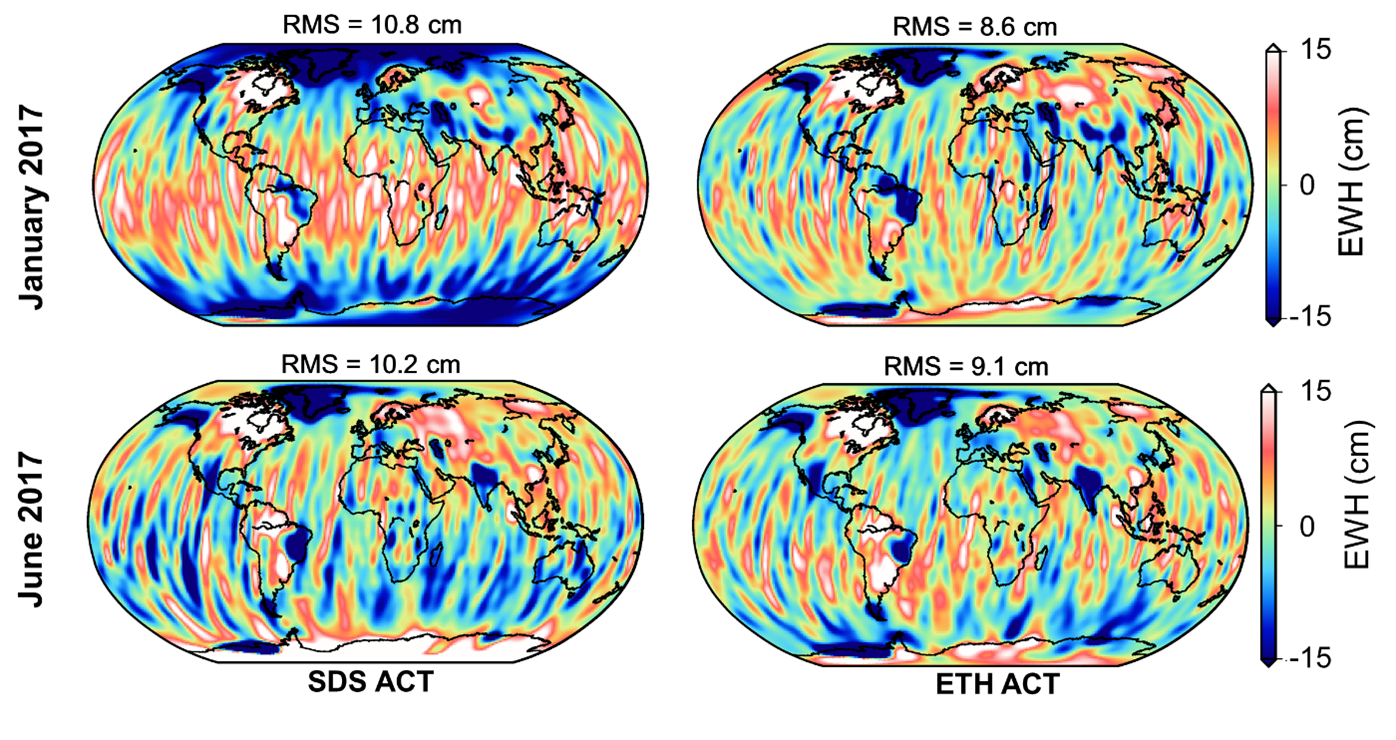
The Group of Space Geodesy is currently investigating the potential of machine learning approaches for handling level-1 data, officially provided by Science Data System (SDS). Currently, we are studying the application of machine learning algorithms for the retrieval of GRACE-B accelerometer data, known as ACT products. Taking advantage of a large available dataset, this work aims to develop a model which can predict the missing data under different orbital conditions. In addition to providing improved solution for the final months of the GRACE satellite mission, the results obtained from the study also offer valuable information that can be used to improve the retrieval of degraded accelerometer data from the Follow-On mission.
Contacts:
Saniya Behzadpour, ETH Zurich,
Benedikt Soja, ETH Zurich,