New publication by Iten et al. (2025)
"Enhanced real-time global ionospheric maps using machine learning" by Iten et al. (2025)
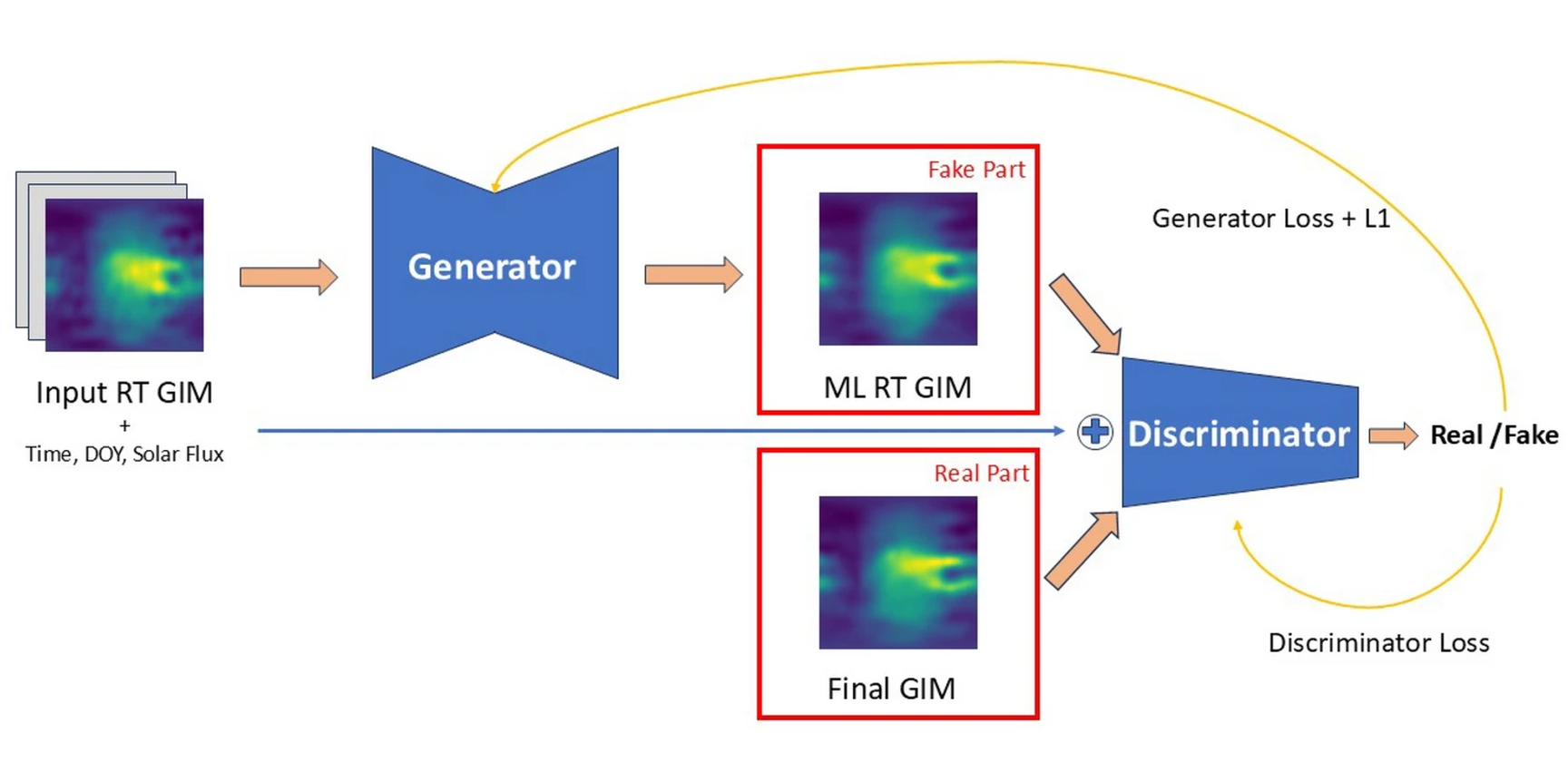
Ionospheric delays are a major source of error in Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), particularly for single-frequency receivers that cannot directly correct these delays. Global Ionospheric Maps (GIMs) help mitigate this issue by describing the ionospheric state. While the International GNSS Service (IGS) provides real-time GIMs, they are less accurate than post-processed final GIMs, which have several days of latency.
In this work, we applied two machine learning techniques, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (cGANs) to enhance the accuracy of existing real-time GIMs. Trained on over 130,000 pairs of real-time and final GIMs, our models learn to map the less accurate real-time maps to their more precise final counterparts. The result is a substantial reduction in ionospheric error, with positioning improvements of up to 21 cm in single-frequency applications, demonstrating the potential of ML to enable more accurate, real-time ionospheric corrections.
Reference
Iten, M., Mao, S., Pan, Y. et al. Enhanced real-time global ionospheric maps using machine learning. GPS Solut 29, 108 (2025). external page https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-025-01858-0