New publication by Crocetti et al. (2024)
"Global, spatially explicit modelling of zenith wet delay with XGBoost" by Crocetti et al. (2024)
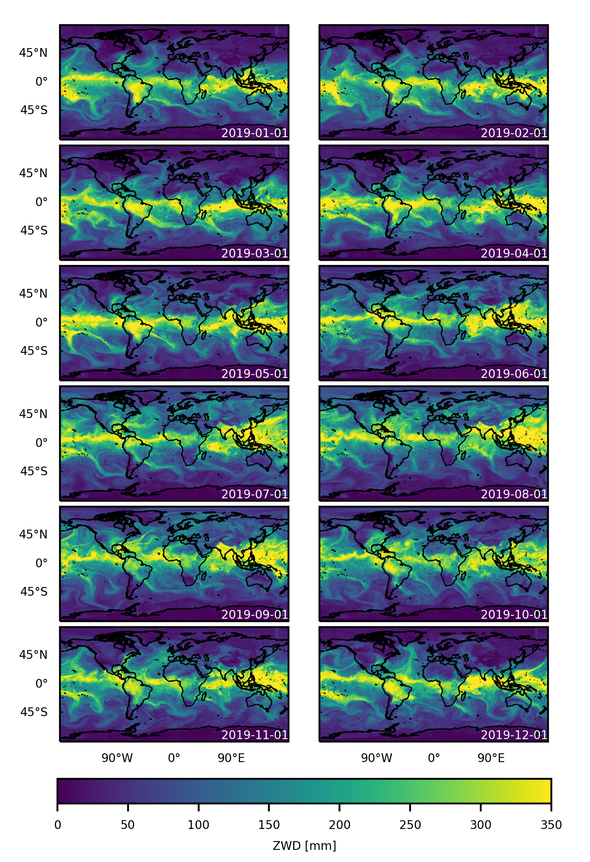
Zenith wet delay (ZWD) is a parameter that we estimate with Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) satellites. It is essential for GNSS positioning because it represents a major source of error. Besides that, it is highly correlated to atmospheric water vapour and thus plays an important role for applications in weather monitoring, forecasting and climate research.
In this study, we present a data-driven, global model of the spatial zenith wet delay (ZWD) field, based on the Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost). The model takes the geographical location, the time, and a number of meteorological variables (in particular, specific humidity at several pressure levels) as input, and can predict ZWD anywhere on Earth as long as the input features are available. It was trained on ZWDs at 10718 GNSS stations and tested on ZWDs at 2684 GNSS stations for the year 2019. Across all test stations and all observations, the trained model achieved a mean absolute error of 6.1 mm, respectively, a root mean squared error of 8.1 mm.
Have a look at the open access article:
external page https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00190-024-01829-2