New publication by Gou et al. (2023)
"Modeling the Differences between Ultra-Rapid and Final Orbit Products of GPS Satellites Using Machine-Learning Approaches" by Gou et al. (2023)
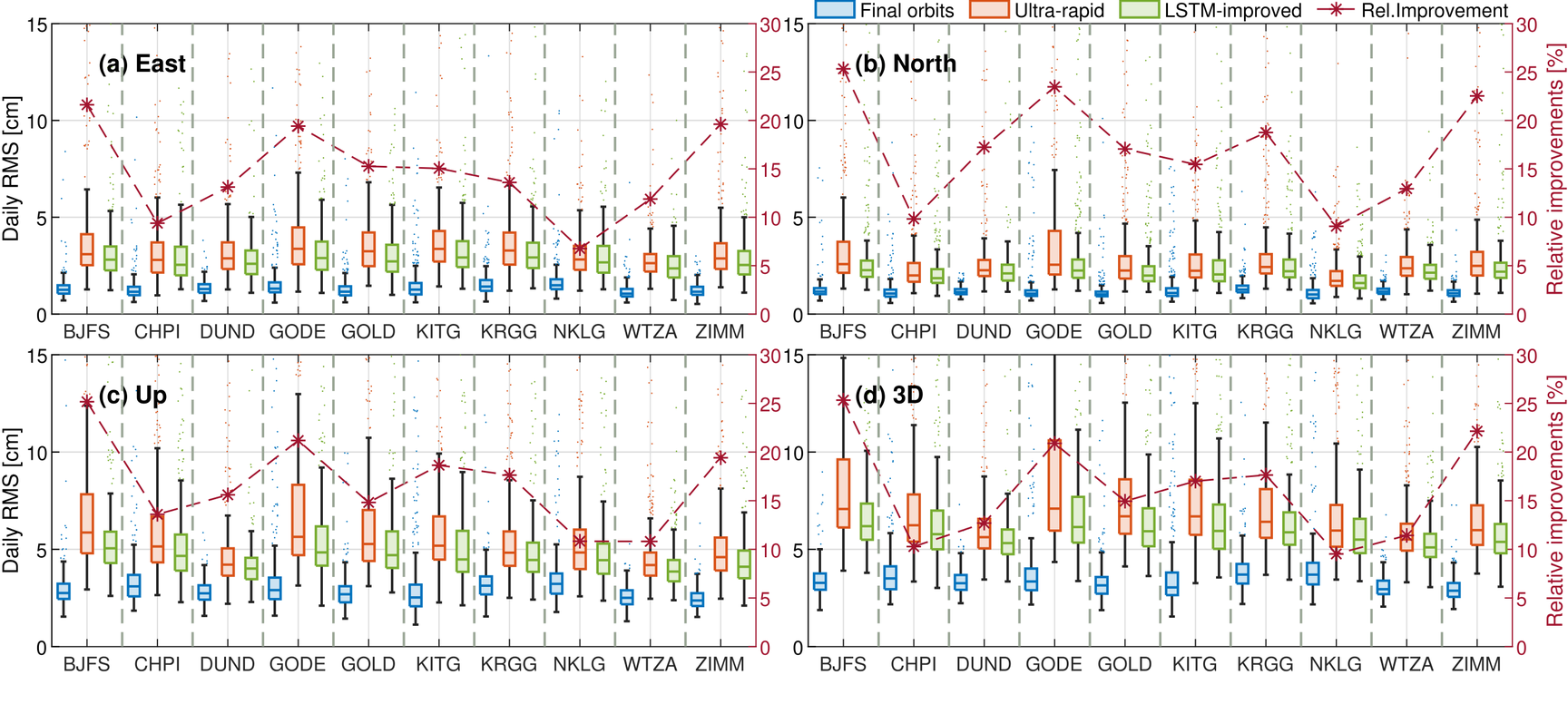
Accurate predictions of GPS satellite orbits are crucial for real-time positioning applications, such as real-time navigation and early warning systems. However, the physics-based orbit predictor cannot perfectly describe the changing perturbing forces, resulting in high errors. In the recent paper published in Remote Sensing, we investigate the potential to use machine learning techniques to further improve the accuracy of the orbit predictions estimated by state-of-the-art physics-based orbit propagators. An average improvement of 47% in 3D RMS is proved. Moreover, the benefits of the improved orbits for positioning applications are also demonstrated with an average improvement of 16% in the accuracy of estimated station coordinates.
For more information, please refer to the external page full paper (open access)